Foundations of Intelligent Learning Agents
CS 747: Foundations of Intelligent Learning Agents, Prof. Shivaram Kalyanakrishnan
1. Reinforcement Learning for Playing Billiards
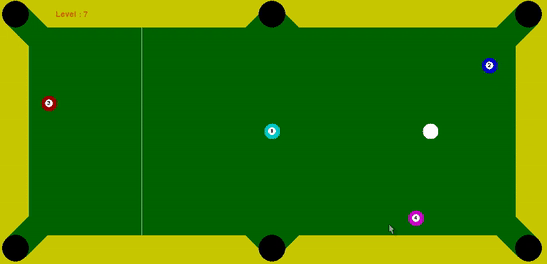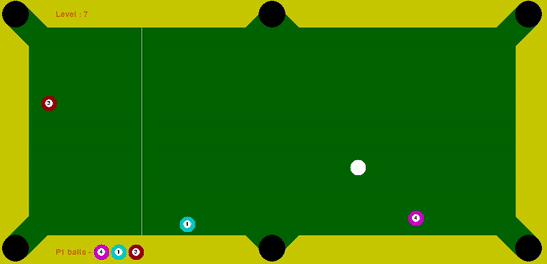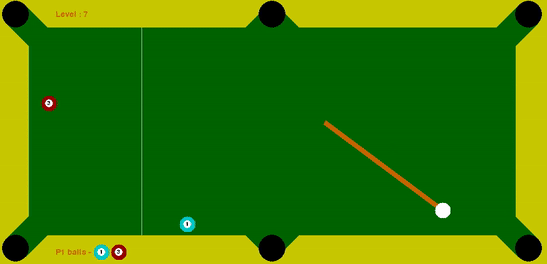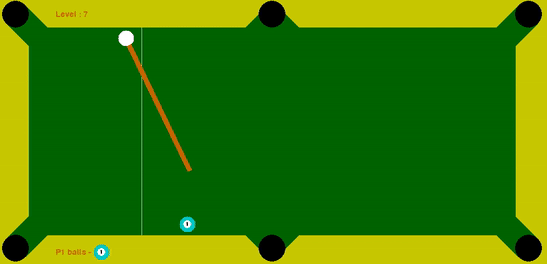
The task of this project is to code an agent that provides us with optimal force and angle at which the cue ball has to be struck, such that it pots all the solid balls within the maximum tries limit. In order to mimic real scenarios where high force to cue ball cultivates to less control, guassian noise proportional to the force is added to the angle provided by the agent to the cue ball.
I coded an agent that employed decision-time planning using Monte-Carlo Tree Search (MCTS) to identify the most suitable ball to pot and to determine the force that should be applied to the ball along with optimal angle. This provides robustness to the Gaussian Noise added to the input angle to the cue ball. I discounted the reward (balls potted) obtained in the future time-step by a factor of 0.25. Thus, by utilizing and discounting the future time-step reward, I established an effective policy for the cue ball.
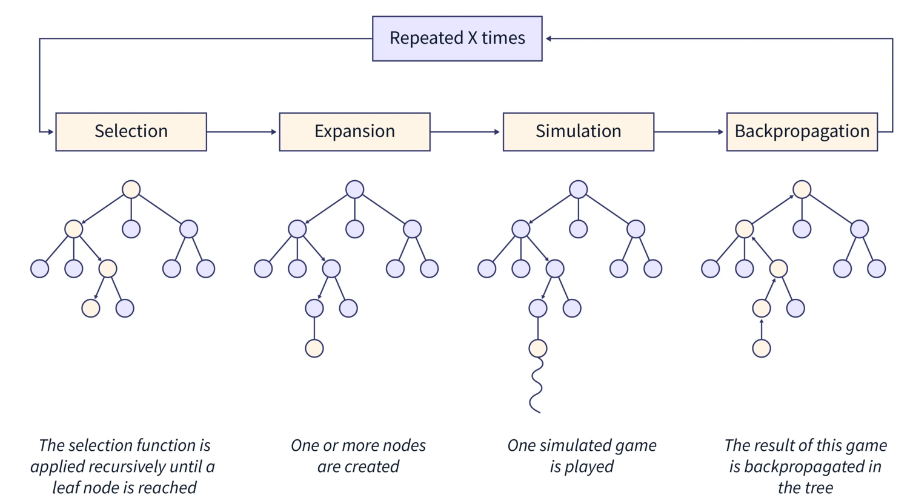
My intermediate experiments that made be realize the importance of tree search, specifically the advantage of tree search for a depth of two when only a single target ball is remaining. Using a depth of two proved to be quite advantageous since the cue ball took an action that had very high probability of potting the single target ball in at max two tries.
2. MDP Planning for Half-Field Offense in Football
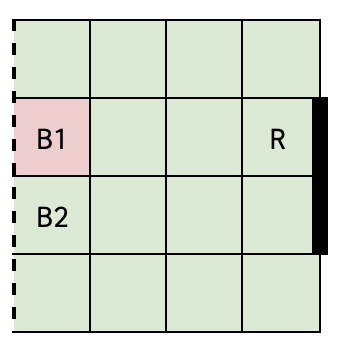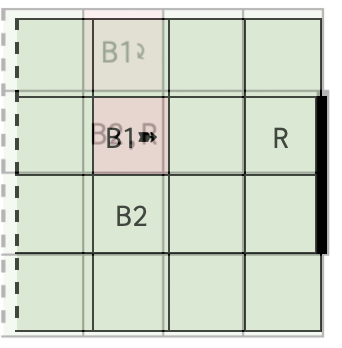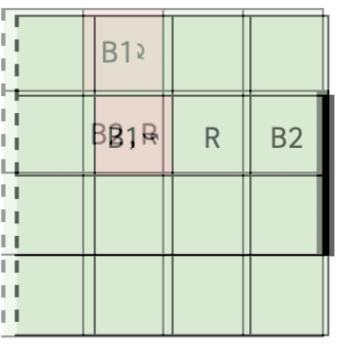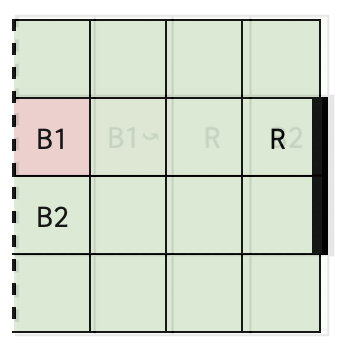
The objective is to formulate an MDP to compute an optimal strategy for scoring goals in a Half Field Offense scenario, where two attackers (B1 and B2) face one defender (R) on a 4x4 grid football pitch with a 2-unit long goal. Skill parameters are defined for each player, which parameterize the player’s success in actions like movement, passing, and shooting, while the opponent adheres to predefined policies (Greedy Defense, Park the Bus, Random Policy).
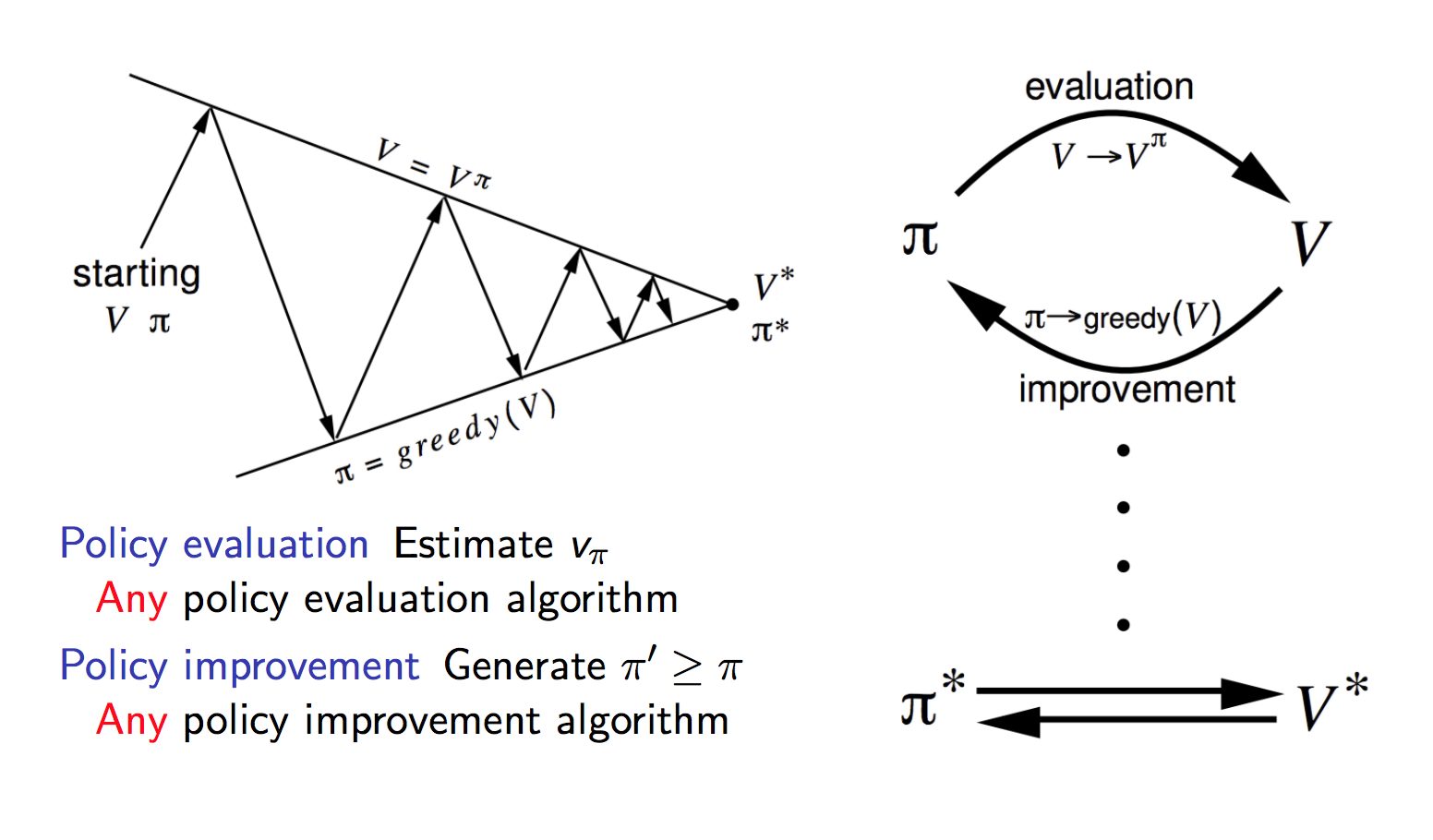
For any input Markov Decision Process (MDP), I coded up a MDP-planner that can use Value Iteration, Linear Programming or Howard’s Policy Iteration to find the optimal policy V* for the MDP. Furthermore using MDP Planning, I devised a strategy to maximize the goal-scoring probabilities for a two-player football team attempting to score a goal against a single opponent in a game of football. In such a formulation of the MDP, my Value function of a state is the expected number of goals starting from the initial state.
3. MDP Planning for Cricket
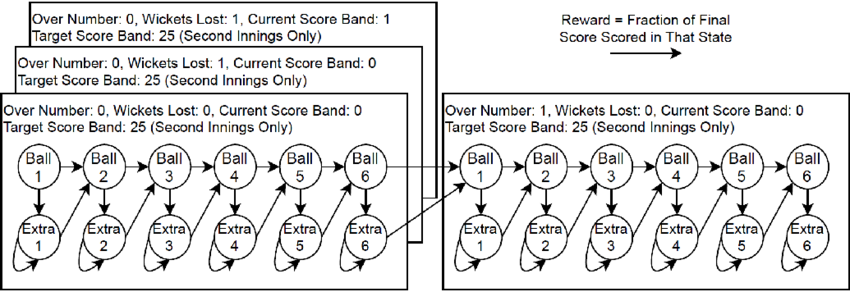
In this task, our goal was to identify an optimal batting strategy for a middle-order batter, referred to as batter A, within the context of a cricket game. In contrast to the agent’s control over the cue ball in the previous project, batter A operates within the dynamics of the game without any influence over a tail-ender ‘B’ and the prevailing game conditions.
The challenge lies in determining the optimal policy for batter A, given the binary outcomes of batter B, who can either get out or score 0/1 runs. The overarching objective is for the batting team to attain a target of T runs within a specified number of balls B.